10.3 Reflection Coefficients
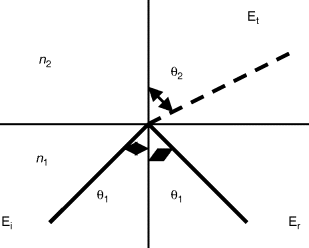
The complex amplitudes of the incident and reflected rays, denoted by Ei and Er respectively in Figure 10.1, are related to each other by
Figure 10.1 Reflection and refraction in two dielectric media.
(10.4) ![]()
where r is the complex reflection coefficient dependent on both the angle of incidence and the polarization of the light ray. The polarization of a light ray is related to the direction of the electric field vector associated with the electromagnetic wave. The transverse electric (TE) condition refers to the situation when the electric fields of the waves are perpendicular to the plane of incidence, that is, the plane containing the wave normal and normal to the interface. Similarly, the transverse magnetic (TM) case occurs when the magnetic field of the wave is normal to the plane of incidence. The reflection coefficients r for the two cases, rTE and rTM, are expressed by the following two Fresnel formulae:
(10.5a) ![]()
(10.5b) ![]()
These two equations may be rewritten, by using Snell's law, Eq. (10.1), as
For any angle of incidence less than ...
Get Silicon Photonics: Fundamentals and Devices now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

