Physical Files in an Oracle Database
A tablespace is a logical view of the physical storage of information in an Oracle database. Three fundamental types of physical files make up an Oracle database:
Control files
Datafiles
Redo log files
Other files, such as password files and instance initialization files, are used within a database environment, but the three fundamental types listed represent the physical database itself. Figure 1-3 illustrates the three types of files and their interrelationships.
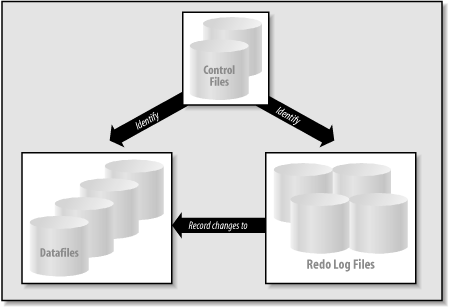
Figure 1-3. The files that make up a database
Oracle9i introduces the concept of Oracle managed files (OMFs). You indicate that you want to use OMFs by specifying values for the initialization parameters DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST and DB_CREATE_ONLINE_LOG_DEST_n (these and all of the Oracle initialization parameters are described in detail in Chapter 2). If you request OMFs, Oracle9i will automatically create, name, and delete (when appropriate) all the files for your Oracle database. OMFs are designed to reduce the maintenance overhead of naming and tracking the names for your Oracle database, as well as to avoid the problems that can occur when fallible human beings do not correctly identify a file in an Oracle database.
The following sections describe the role of these three types of files and their interactions.
Get Oracle in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

