1.4 OPTICAL SPACE CHANNELS
In the optical space systems in Figure 1.5 the laser source produced an optical field that is intended for a receiving area that is located a significant distance away. This distance is usually far enough so that the laser source appears as a point source when viewed from the receiver. Systems in which this point source assumption can be made can be analyzed similar to RF communications.
If the source producing the optical field is a point source, operating in a free space medium and modulated with the field function in Eq. (1.3.6), then the field at a remote point ξ due to this source is given by
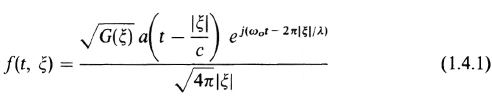
where |ξ| is the distance to the point ξ, λ is the source wavelength corresponding to the frequency ω0, c, is the speed of light, and G(ξ) is the transmitter power gain in the direction ξ. Equation (1.4.1) describes an optical field that propagates out from the source as a spherical wave with diminishing amplitude. However, to an area A located a distance z away, where z » A1/2, all points on A are approximately the same distance from the source. Thus |ξ| is the same over A and the field arriving at A from the point source is basically a plane wave field. That is, the field emminating from a point source appears as a plane wave when observed by a small area from a remote distance. The field intensity at a point ξ in A is then
where Gt is the transmitting optics ...
Get Optical Communications, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

