Stored Functions
Stored functions are similar to stored procedures: they are named program units that contain one or more MySQL statements. They differ from procedures in the following ways:
The parameter list of a function may contain only
INparameters.OUTandINOUTparameters are not allowed. Specifying theINkeyword is neither required nor allowed.The function itself must return a single value, whose type is defined in the header of the function.
Functions can be called from within SQL statements.
A function may not return a result set.
Generally, you should consider using a stored function rather than a stored procedure when you have a program whose sole purpose is to compute and return a single value or when you want to create a user-defined function for use within SQL statements.
Figure 2-16 shows a
function that implements the same functionality found in the discount_price stored procedure we created
earlier in this chapter.
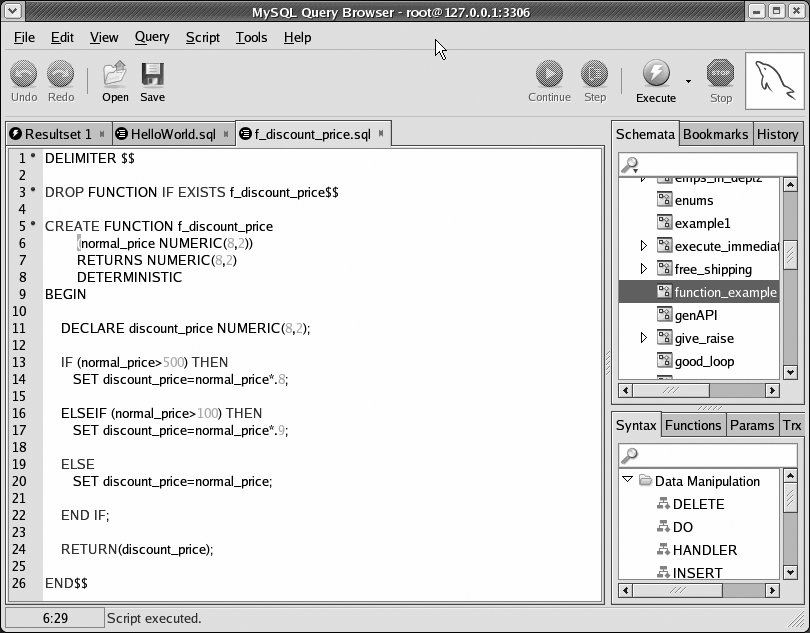
The following table explains a few things that set apart this function from its stored procedure equivalent:
Line | Explanation |
7 | Specify a |
8 | MySQL applies stricter rules to
stored functions than it does to procedures. A function must
either be declared not to modify SQL (using the |
Get MySQL Stored Procedure Programming now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

