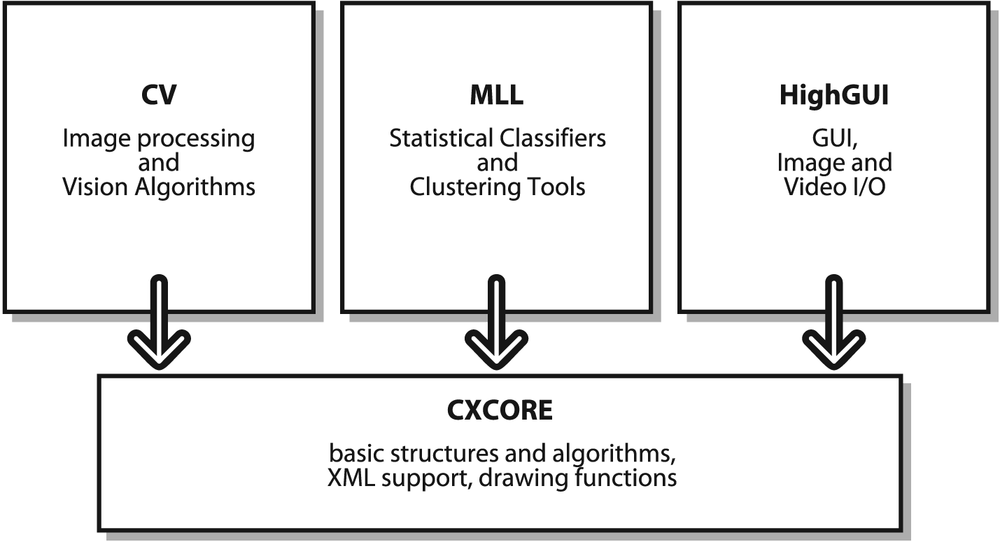
OpenCV is broadly structured into five main components, four of which are shown in Figure 1-5. The CV component contains the basic image processing and higher-level computer vision algorithms; ML is the machine learning library, which includes many statistical classifiers and clustering tools. HighGUI contains I/O routines and functions for storing and loading video and images, and CXCore contains the basic data structures and content.
Figure 1-5 does not include CvAux, which contains both defunct areas (embedded HMM face recognition) and experimental algorithms (background/foreground segmentation). CvAux is not particularly well documented in the Wiki and is not documented at all in the …/opencv/docs subdirectory. CvAux covers:
Eigen objects, a computationally efficient recognition technique that is, in essence, a template matching procedure
1D and 2D hidden Markov models, a statistical recognition technique solved by dynamic programming
Embedded HMMs (the observations of a parent HMM are themselves HMMs)
Extensions to Delaunay triangulation, sequences, and so forth
Stereo vision
Shape matching with region contours
3D tracking
Finding skeletons (central lines) of objects in a scene
Warping intermediate views between two camera views
Video surveillance (see Wiki FAQ for more documentation)
Camera calibration C++ classes (the C functions and engine are in CV)
Some of these features may migrate to CV in the future; others probably never will.
Get Learning OpenCV now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.