Google makes an excellent phonebook, even to the extent of doing reverse lookups.
Google combines residential and business phone number information and its own excellent interface to offer a phonebook lookup that provides listings for businesses and residences in the United States. However, the search offers three different syntaxes, different levels of information provide different results, the syntaxes are finicky, and Google doesn’t provide documentation.
Google offers three ways to search its phonebook:
-
phonebook Searches the entire Google phonebook
-
rphonebook Searches residential listings only
-
bphonebook Searches business listings only
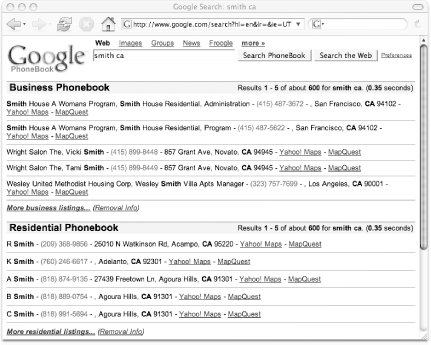
Using a standard phonebook requires knowing quite a bit of information about what you’re looking for: first name, last name, city, and state. Google’s phonebook requires no more than last name and state to get it started. Casting a wide net for all the Smiths in California is as simple as:
phonebook:smith ca
Try giving 411 a whirl with that request! Figure 1-17 shows the results of the query.
Notice that, while intuition might tell you that there are thousands of Smiths in California, the Google phonebook says that there are only 600. Just as Google’s regular search engine maxes out at 1,000 results, its phonebook maxes out at 600. Fair enough. Try narrowing down your search by adding a first name, city, or both:
phonebook:john smith los angeles ca
At the time of this writing, the Google phonebook found 2 business and 20 residential listings for John Smith in Los Angeles, California.
The phonebook syntaxes are powerful and useful, but they can be difficult to use if you don’t remember a few things about how they work.
The syntaxes are case sensitive.
Searching for
phonebook:john doe caworks, whilePhonebook:john doe ca(notice the capital P) doesn’t.Wildcards don’t work.
Then again, they’re not needed, since the Google phonebook does all the wildcarding for you. For example, if you want to find shops in New York with “Coffee” in the title, don’t bother trying to envision every permutation of “Coffee Shop,” “Coffee House,” and so on. Just search for
bphonebook:coffee new york nyand you’ll get a list of any business in New York whose name contains the word “coffee.”Exclusions don’t work.
Perhaps you want to find coffee shops that aren’t Starbucks. You might think
phonebook:coffee-starbucksnewyork nywould do the trick. After all, you’re searching for coffee and not Starbucks, right? Unfortunately not; Google thinks you’re looking for both the words “coffee” and “starbucks,” yielding just the opposite of what you were hoping for: everything Starbucks in NYC.ORdoesn’t always work.You might start wondering if Google’s phonebook accepts
ORlookups. You then might experiment, trying to find all the coffee shops in Rhode Island or Hawaii:bphonebook:coffee (ri |hi). Unfortunately that doesn’t work; the only listings you’ll get are for coffee shops in Hawaii. That’s because Google doesn’t appear to see the(ri|hi)as a state code, but rather as another element of the search. So if you reversed your search above, and searched forcoffee(hi|ri), Google would find listings that contained the string “coffee” and either the strings “hi” or “ri.” So you’ll find Hi-Tide Coffee (in Massachusetts) and several coffee shops in Rhode Island. It’s neater to useORin the middle of your query, and then specify your state at the end. For example, if you want to find coffee shops that sell either donuts or bagels, this query works fine:bphonebook:coffee(donuts|bagels)ma. That finds stores that contain the word “coffee” and either the word “donuts” or the word “bagels” in Massachusetts. The bottom line: you can use anORquery on the store or resident name, but not on the location.
All three phonebook syntaxes support
reverse lookup, though it’s probably best to use the
general phonebook: syntax to avoid not finding
what you’re looking for due to its residential or
business classification.
To do a reverse search, just enter the phone number with area code. Lookups without area code won’t work.
phonebook:(707) 827-7000
(This is the phone number of O’Reilly world headquarters in Sebastopol, California, USA.)
Note that reverse lookups on Google are a hit-or-miss proposition and don’t always produce results. If you’re not having any luck, consider using a more dedicated phonebook site such as WhitePages.com (http://www.whitepages.com/).
While Google’s phonebook is a good starting point, its usefulness is limited. If you’re looking for a phone number at a university or other large institution, while you won’t find the number in Google, you certainly can find the appropriate phonebook, if it’s online.
If you’re looking for a university phonebook, try
this simple search first: inurl:phone
site:university.edu,
replacing university.edu with the domain
of the university you’re looking for. For example,
to find the online phonebook of the University of North Carolina at
Chapel Hill, you’d search for:
inurl:phone site:unc.edu
If that doesn’t work, there are several variations
you can try, again substituting your preferred
university’s domain for
unc.edu:
title:"phone book" site:unc.edu(phonebook | "phone book") lookup faculty staff site:unc.eduinurl:help (phonebook | "phone book") site:unc.edu
If you’re looking for several university phonebooks,
try the same search with the more generic site:edu
rather than a specific university’s domain. There
are also web sites that list university phonebooks, one of which is
the Phonebook Gateway Server Lookup (http://www.uiuc.edu/cgi-bin/ph/lookup), with
over 330 phonebooks.
Get Google Hacks, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.