How architecture evolves into strategy
A look at the roles of architect and strategist, and how they help develop successful technology strategies for business.
 Sketch (source: Pixabay)
Sketch (source: Pixabay)
There are two jobs in the world that people want to do the most while knowing the least about: architect and strategist.
I should start by saying this section does not offer a treatise on how to do architecture. I’m offering an overview of my perspective on the field, which I hope is a unique and interesting take on it, in order to provide context for the work at hand: devising a winning technology strategy for your business.
Technology systems are difficult to wrangle. Our systems grow in accidental complexity and complication over time. Sometimes we can succumb to thinking other people really hold the cards, that they have the puppet strings we don’t.
This is exacerbated by the fact that our field is young and growing and changing, and we’re still finding the roles we need to have to be successful. To do so, we borrow metaphors from roles in other industries. The term “data scientist” was first used in the late 1990s. In 2008 or so, when data scientist emerged as a job title, it was widely ridiculed as a nonjob: the thought that people who just worked with data could be scientists, or employ the rigors of their time-honored methods, was literally laughable in many circles. By 2012, Harvard Business Review published an article by Thomas Davenport and D.J. Patil called “Data Scientist: The Sexiest Job of the 21st Century.” Today, it’s one of the most desired jobs, with pundits declaiming the terrifying state that we do not have nearly enough of them to tackle our most central technology problems.
Likewise, the term “architect” didn’t enter popular usage to describe a role in the software field until the late 1990s. It, too, was ridiculed as an overblown, fancy-pants misappropriation from a “real” field. Part of the vulnerability here is that it hasn’t always been clear what the architect’s deliverables are. We often say “blueprints,” but that’s another metaphor borrowed from the original field, and of course we don’t make actual blueprints.
With such origins, and with the subsequent division of the architect role into enterprise architect, solution architect, data architect, and so forth, the lines have blurred further. The result is that decades later, the practice and the art of the architect in technology varies dramatically not only from one company to the next but also from one department and one practitioner to the next.
So, we will define the role of the architect in order to proceed from common ground. This is my tailored view of it; others will have different definitions. Before we do that, though, let’s cover some historical context that informs how we think of the role.
Vitruvius and the principles of architecture
Architecture begins when someone has a nontrivial problem to be solved. The product management team states what must be done to solve the problem, and the architect describes how to realize that vision in a system.
The first architect of record is a fellow named Vitruvius, who worked as a civil engineer in Rome in the first century B.C. While you may not know his name, during the Renaissance, Leonardo da Vinci popularized the “Vitruvian Man” with perfect proportions based on Vitruvius’s ideas. Everyone who goes to architecture school learns his work.
Vitruvius is the author of de Architectura, known today as Ten Books on Architecture. It’s a delightful, engaging read and had a strong influence on Renaissance artists such as Michelangelo and da Vinci. In it, Vitruvius expands on the three requirements any architecture must demonstrate:
- Firmitas
- It must be solid, firm.
- Utilitas
- It must be useful, have utility.
- Venustas
- It must be beautiful, like Venus, inspiring love. This is sometimes translated as “delightful.”
It’s a given that we must design a system, including a local software architecture, that actually runs, that is “solid.” It may need to run for many years, even decades, and be maintainable to adapt to changes over that time. Solid doesn’t mean inflexible. Skyscrapers are built on purpose to sway slightly with the wind, specifically to be more durable. The Sears Tower in Chicago regularly sways between six inches and a foot; taller buildings in America sway as much as four to five feet. Your architectures, and your strategies, must be similarly flexible in order to endure. We’ll look at this later when we discuss how to support evolutionary architectures through our strategies.
It must also be fit to purpose, which means understanding deeply what the real purpose of the system is and how to manage user expectations. This is supported in real terms through standards and consistent application of conventions, both in the information architecture (i.e., the user experience and design) and within the software construction itself.
Beauty, for Vitruvius, isn’t really in the eye of the beholder. It is about harmony of proportion. One suggestion we can deduce from this for our current purposes is that we must rightsize our architecture and strategy work for the task at hand.
Vitruvius states—without irony—that an architect must concern himself with and become educated in several diverse fields of study, such that they find their way into the work. He outlines them in Chapter 1 of de Architectura:
- Skill in manual labor as well as in theory
- Proclivity and desire for continuous learning
- A dexterity with tools
- An understanding of optics—how the light gets in
- History, such that you can emphasize and not misinterpret signs of cultural significance
- A strong understanding of philosophy, in order to practice abstract thinking as well as honesty and courtesy
- Physics, to help make things sturdy
- Art, music, theater, drawing, painting, and poetry, to help make things beautiful and well suited to their human purposes
- Math
- Medicine
- Astronomy
- Politics
He concludes that absent a degree of education and even lay practice in any one of these areas, one cannot refer to oneself as an architect. These are excellent guides for us in technology today. For those of us concerned with the business of making software and setting the direction for other technologists, to hold ourselves to account in these ways would serve us very well.
In a recent conversation I had with Ben Pring, philosopher, noted futurist, and director of The Future of Work Center at Cognizant, he underscored the importance of beauty in software, pointing out that historically our most culturally significant buildings have been not merely adorned but specifically built with beauty in mind as a central, driving narrative. I conclude from this that such foregrounding reinforces in the popular imagination the power of the institutions that build them. I base this conclusion on the preface in the Ten Books, in which Vitruvius writes openly and directly to Emperor Caesar, stating:
But when I saw that you were giving your attention not only to the welfare of society in general and to the establishment of public order, but also to the providing of public buildings intended for utilitarian purposes, so that not only should the State have been enriched with provinces by your means, but that the greatness of its power might likewise be attended with distinguished authority in its public buildings, I thought that I ought to take the first opportunity to lay before you my writings on this theme. (emphasis mine)
Realizing these broad dicta into an architecture means, I think, finding the concentrations of power, and determining how to best support and ultimately inspire the human factor in the forms we create. I hope once you’re done with this book, you’ll have some ideas for how to enable and reveal the three facets of firmitas, utilitas, and venustas in your own work.
Three concerns of the architect
Whereas developers are typically focused on delivering working code for a user story within the next two weeks for one system within their one team, architects are concerned with how technology can fulfill business goals given a long-term outlook across a variety of interrelated systems across many teams. It’s analogous to a project view versus a portfolio view. They should have their visors raised much higher. The architect is hopefully not concerned with low-level details of the code itself inside one system but is more focused on where data center boundaries are crossed, where system component boundaries are crossed.
Here’s my definition of an architect’s work: it comprises the set of strategic and technical models that create a context for position (capabilities), velocity (directedness, ability to adjust), and potential (relations) to harmonize strategic business and technology goals. Notice that in this definition, the role of the architect and technology strategist is not to merely serve the business but to play together. I have been in shops where technology was squarely second fiddle, a subservient order-taking organization to support what was deemed the real business. That’s no fun for creative people who have something to contribute. But more importantly, I submit that businesses, now more than ever, cannot sustain such a division and to create greater competitive advantage must work toward integration with co-leadership.
Over my 20 years in this field, I’ve come to conclude that there are three primary concerns of the architect:
- Contain entropy.
- Specify the nonfunctional requirements.
- Determine trade-offs.
There are many different roles that architects legitimately play in organizations. But the primary struggle I have seen comes when they are not focused on a deliverable, on what could be conceived as a “blueprint.” Without that focus, they tend to weigh in at project meetings or make declarations informally that can’t be remembered or followed. To stay pertinent to the project, and to help guide it in a way that others may not have the purview to do, drawing a line at these boundaries seems to work out pretty well. The definition remains, of course, rather open to interpretation, in grudging deference to the machinations of the real world.
Let’s unpack each of those responsibilities.
Contain entropy
This viewpoint on the architect’s work I learned in a fun conversation over dinner in New York with the very smart and funny Cameron Purdy, the founder of Coherence, who at the time ran Java at Oracle. “Entropy” refers to the second law of thermodynamics, which roughly states that systems over time will degrade into an increasingly chaotic state, such that the amount of energy in the system available for work is diminished.
The architect defines standards, conventions, and tool sets for teams to use. These are common practices and are generally idiosyncratic to any given organization. As application or solution architects, they help within a system, within an ecosystem, and across an organization to create a common set of practices for developers that help things both go more quickly and be more understandable and maintainable. This is a form of containing entropy. As we mature, we realize that picking one tool or framework or language or platform is not a matter of personal taste but rather a choice with broad ramifications for future flexibility, mergers and acquisitions, training, our ability to hire future supporting teams, and our future ability to directly support—or subvert—the business strategy.
Those with more business-oriented concerns and technologists cannot ignore each other’s fields. Working as a patternmaker and a synthesizer, the architect-as-strategist broadens and ennobles these concerns, creating technology strategies that both are rooted in the causes and concerns of the business and recognize its constraints and opportunities. In collaboration with product management and with colleagues in strategy, business development, finance, and HR, the architect works to ensure there is alignment between the systems, yes, but also between those systems and the organization, and between the organization and its stated aims.
In short, for far too long we architects have thought we were in the business of making software. But we’re in the business of building a business.
The architect who is containing entropy is stating a vision around which to rally, showing a path in a roadmap, garnering support for that vision through communication of guidelines and standards, and creating clarity to ensure efficiency of execution and that you’re doing the right things and doing things right.
I love this definition of containing entropy because it offers something to both the software-minded and the business-minded architect (which I hope are two categories this book will help to collapse). One cannot be successful as an architect without thinking of not only what to do but how to get it done within an organization, which requires knowing why it should matter to someone who isn’t a technologist.
We often hear of architects with failed dreams of how the system should have been. They are consumed by writing documents, and those documents are subsequently ignored, leading them to give up. Left with only the most informal conversational avenues to offer insufficient direction to teams, they become frustrated and even marginalized.
Knowing that you’re in the business of building a business, and that technology is just an avenue by which you enable that, is a critical first step to being not only useful but powerful as an architect and strategist.
Specify nonfunctional requirements
Knowing what you’re on the hook for, letting others know it, and making sure that it’s a concrete deliverable will all go a long way to ensuring your vision is understood and realized.
Product management is responsible for specifying what the system must do for the end user. They might state functional requirements in user stories and epics.
The nonfunctional requirements are properties of the system that do not necessarily appear directly to the user. They are typically described as the “-ilities.” The ones I focus on most are scalability, availability, maintainability, manageability, monitorability, extensibility, interoperability, portability, security, and performance.
The architect is responsible for specifying how the system will realize the functional and nonfunctional requirements in its construction. In order to do so, she must write a document that specifies how these will be realized.
This document, the architecture definition, serves as the technologist’s answer to the blueprint. It should be structured in four broad categories to include business, application, data, and infrastructure perspectives and expressed with clarity and decisiveness, using primarily testable statements as valid propositions (which we’ll examine in the next chapter) and math.
Finding ways to make those expressions concrete and executable is too often overlooked. In addition to writing and publishing a formal architecture definition document to the teams, you can do this by adding nonfunctional requirements to user stories as acceptance criteria.
Determine trade-offs
You can never try to escape one danger without encountering another. Prudence consists in recognizing the different dangers and in accepting the least bad as good.
—Machiavelli, The Art of War
As we know, every action produces an equal and opposite reaction. Adding security reduces performance. Sharding and partitioning the database affords greater performance and distribution but creates complexity that is difficult to manage. Adding robust monitoring can generate huge volumes of log data to be stored, rotated, secured, and cleansed. Keeping the design “simple” often defers the interests of flexibility until later, where it becomes very expensive.
The role of the architect is to see where those challenges may lurk, seek to make them explicit, and make value judgments about how to balance the solutions and the new problems they occasion, under the guidance of the broader business strategy. As English poet John Milton wrote in Paradise Lost, you make “the darkness visible.”
In short, you’re never quite solving a problem. You’re only trading it for one that you’d rather have. We solve our need for shelter by assuming a mortgage for which we then must pay. Paul Virilio, the French cultural theorist and philosopher, reminds us lucidly, “When you invent the ship, you also invent the shipwreck…Every technology carries its own negativity, which is invented at the same time as technical progress” (Politics of the Very Worst, Semiotexte). Your architecture and strategy work will do well to examine not only how you are addressing the problems you’ve been given but also what new problems your solutions precipitate.
Any trade-off eventually reduces to a trade-off of time and money.
Absent a strategic mindset, many technologists left to their own devices create what amounts to little more than shopping lists of shiny objects. These can include the latest and most fashionable tech because it’s popular or because it might bolster their résumé. We hear this frequently described as “a solution looking for a problem.” Moreover, the less shallow or cynically minded among us are still rather prone to chasing exciting technology for its own sake, not unlike a dog chasing a squirrel. Intellectual curiosity is a wonderful thing, a best thing. But to ensure your technology and architecture decisions are truly supportive of the business—that is, give it the best chance to create competitive advantage—they need to be not shopping lists of shiny objects but squarely strategic.
So, let’s look at the role of the strategist.
The Strategist’s Role
Strategy is about getting more power than the starting position would suggest. Strategy is the art of creating power.
—Lawrence Freedman, Strategy: A History (Oxford University Press)
The word “strategy” originates from the Greek strategos. The term first appeared in fifth-century Athens as a conflation of the words meaning the expansion of the military general and came to be used to refer to the offices or science of the general—the general’s work. But the word strategy entered general use only at the start of the 19th century in Antoine-Henri Jomini’s writing on Napoleon’s methods.
Jomini was of Swiss origin; he started out as a banker in Paris, later joined the French army under Napoleon, and eventually got promoted to general. Jomini began writing down Napoleon’s methods in such a lucid manner that they came to be published as a book, entitled Treatise on Major Military Operations, in 1803. Jomini’s strategies were employed in the U.S. Civil War and eventually taught at West Point Academy. He is considered the founder of modern strategy by many military historians.
Jomini’s definition of strategy helpfully divides the word. He writes, “Strategy decides where to act; logistics brings the troops to this point; tactics decides the manner of execution.” In other words, means (resources) are allocated and subjected to a method in order to achieve a goal.
Yet definitions of strategy vary. One of the more abstract definitions comes from Sun Tzu, a Chinese general and philosopher and author of The Art of War in 500 B.C. His book was not translated into English until the 20th century, at which point it began serving as a foundational text for guiding military strategies. It entered the popular imagination once it got adapted and marketed for business purposes.
In it, he writes, “Strategy is the art of making use of time and space.” This is a tall order, and while aesthetically I appreciate the definition, we can break this down further in order to come to something practically executable.
Note
The History of Strategy
If you’re interested in the intellectual history of strategy, its origins, and its evolution from military thought to game theory to business, I highly recommend Lawrence Freedman’s “Strategy: A History” (Oxford University Press). It’s a fascinating read and offers a much richer view than we need here.
For our purposes, strategy is about determining the problems and opportunities in front of you, defining them properly, and shaping a course of action that will give your business the greatest advantage. Balancing problem solving with creating and exploiting new opportunities through imagination and analysis is the cornerstone of a great strategy.
Echoing Jomini, we’ll say that strategy is about determining the best balance between a set of goals, the method used to achieve them, and the resources available as means. With the current rate of change in business, we can’t set it and forget it, expecting that a three- or five-year strategy will go unrevised. At the same time, constant revision amounts to a reactionary collection of tactics, which is no strategy at all.
Most business strategies will concern themselves with the following:
- The goals of the organization
- The operating model: processes and how your company conducts its business
- Culture: the mores and value system, the modes of communication
- Talent strategy: how you source and retain talent, how you train them
- Facilities strategy: where you do business, relevant local laws, and cost concerns
Strategies should be created at different levels: broad corporate-level strategies, business unit or division strategies, departmental strategies, and portfolio strategies. These will be more or less formal and be revised more frequently according to the climate and what life-cycle stage you find yourself in.
The Triumvirate: Strategy, Culture, and Execution
Culture eats strategy for breakfast.
—Management professor Peter Drucker
Any business aims to do one or many of these things:
- Grow shareholder value
- Grow earnings per share
- Increase revenue
- Manage costs
- Diversify or create new revenue streams
- Cross-sell more products
- Increase market share
- Increase share of wallet
- Increase yield
- Improve customer retention
- Reduce product error/defect rates
- Improve safety
- Improve time to market/speed of operations
- Grow through acquisition
Of course, there are different emphases at different times. To achieve these aims, broadly speaking, the strategist asks these questions:
- Are resources devoted to the right areas, to the most important customers?
- Are we creating products and services that can thrive in a market in different time horizons?
- Where should we spend money? Where should we cut costs?
- Where do skills need to be added or strengthened?
- Where can productivity be improved?
- What culture, attitude, and skills are required?
Many companies have a chief strategy officer or VP of corporate strategy. Strategy season frequently begins in the spring, giving this person and her team a couple of months to prepare a deck to present to the executive leadership team in the late summer. This will be discussed, revised, and eventually approved and used as input for budget season, which begins in the fall and continues until the budget for the following year is approved. We in technology tend to like to see our ideas realized moments after we have them. Being aware of this calendar and corporate planning process will help you plan for adding any big-ticket items to the slate in time for them to receive the necessary attention, support, and budget allocations.
That said, the evolution of Agile software methods, the preponderance of “disruptive” startups, and a growing global economy have all aligned variously to dilute the formality and rigidity of the strategist’s role in such a process, leading her to rely more on regular conversations with the executive team and create reports with tighter scopes on an ongoing basis.
Depending on her level of power and position within the organization, the strategist finds herself concerned with some or all of the following:
- Identifying business development opportunities, such as partnerships, joint ventures, cooperative arrangements with competitors, and the like
- Finding, proposing, and validating mergers and acquisition opportunities
- Building strategic capabilities within certain areas of the organization, such as helping create a sustainable AI practice in the face of growing trends
- Performing research based on data to recommend long-term directions for the company (generally 1–3 years)
This last one is very common and how many strategists are trained as consultants entering the field at the venerable strategy firms such as Bain, Boston Consulting Group (BCG), and McKinsey. They likely work with business analysts, marketing, sales, technology, and operations teams in a cross-functional working group to develop hypotheses for how the business climate might be enabling or impinging upon their competitive advantage and how they should define a goal and direction and allocate resources to win in the marketplace.
According to one McKinsey report, 40% of strategists responding to their survey are most focused on “using fact-based analysis to spot industry shifts and to understand their own companies’ sources of competitive advantage as a foundation for clear, differentiated strategies.”
But spending months researching and creating data-driven decks is no longer enough. Because the world is moving so fast, the traditional strategist has taken the driver’s seat in building capabilities. As the walls between business and technology continue to fold in on each other, the strategist may well find himself leading a team of data scientists to create an analytics platform to help themselves and their customers gain precious insights into their business operations. My colleague Balaji Krishnamurthy, the VP of strategy at Sabre Hospitality, who was previously in strategy roles at McKinsey and LinkedIn, offers this observation:
To be a good strategist, you need to be ready to deal with ambiguity. You need to be ready to pivot. You must form a hypothesis quickly about what must be done, then synthesize a lot of data. You must then see options and possibilities available, determine a goal, and present your findings clearly with a recommendation on how to allocate resources to achieve that goal.
Ultimately, companies are looking to grow and gain some distinctive competitive advantage. They can do this through technical innovation properly applied to real-world business problems. One assertion of this book is that the roles of chief architect and chief strategist are more blurred, and more aligned, than ever and that their mutual understanding of each other’s concerns and methods will be an increasingly important driver for winning organizations.
Learn from your executive and product leadership teams what areas of focus they have for their business strategy and product roadmaps, so you can be prepared to match your technology to them.
For example, if your business is in cost-cutting mode, as companies tend to be when revenue is soft or they’re preparing for an IPO, then your technology strategy should match. You can do that by examining the people angle: can you move workers or ramp down in expensive cities in order to hire programmers in lower-cost development centers? Can you examine your delivery and release processes to add automation and reduce manual labor there? Can you use free and open source libraries in place of expensive commercial software? These are examples from people, processes, and technical perspectives of how you can map your technology strategy to the business strategy.
A strategy deck is analogous to an architecture definition document for the organization. Neither will achieve the desired aims if you assume it lives in a vacuum.
The culture of your organization comprises your stated principles and to a far greater extent, the actual lived principles as reflected by the attitudes, communication styles, and behaviors of your teams. If your teams are territorial and competitive, an integrative platform strategy must identify and address that challenge.
Finally, your teams must be ready and capable of executing on your strategy. A strategy deck that states lofty, exciting aims will fail if it also doesn’t include diligent, consistent execution and clear metrics to measure its success. This triumvirate is illustrated in Figure 1.
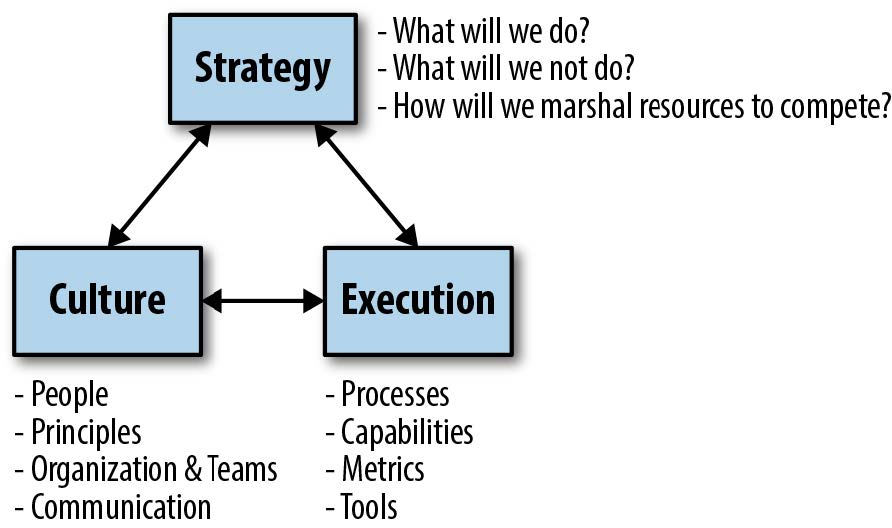
Find ways to work with your leadership and across teams to ensure all of these forces are aligned. A good first step for doing so is to create two versions of the strategy: one that provides an honest and detailed examination of all three factors to share with the executive team and another shorter version that communicates only the changes you’re driving in a way that you can share publicly with teams. In long-range planning, there are financial, business transaction, and personnel matters that obviously can’t be disclosed.
