10.9 CONCLUSIONS
In this chapter, the clustered and scattered look-ahead pipelining methodologies have been applied to pipeline the 1st-order and higher order IIR digital filters. This chapter also addressed the design of parallel IIR filters. The incremental block processing approach has been used to design low-area parallel architectures for higher order IIR filters. Pipelining of lattice recursive digital filters is addressed in Chapter 12. Pipelining and parallel processing can be exploited to either increase the sampling speed or lower the supply voltage at the same speed to reduce power consumption. Look-ahead can also be used for concurrent implementations of dynamic programming problems [19] (see Problem 25), Viterbi decoders [20], and quantizer loops [21]. Different forms of relaxations of the look-ahead including sum, product, and delay relaxations, were used to derive a family of pipelined topologies for LMS and stochastic-gradient lattice adaptive digital filters. Pipelining of few other types of adaptive digital filters is addressed in [22]. Pipelining of recursive least square (RLS) adaptive digital filters using scaled tangent rotation (STAR) is addressed in [23] and using annihilation-reordering look-ahead is addressed in [24].
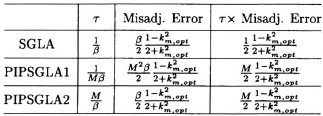
Table 10.2 Comparison of Misadjustment Errors for Different SGLA Architectures
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

