where [𝒮𝒟(xk)]i0 is the ioth component of 𝒮𝒟(xk) (which sorts the components of |xk| into decreasing order) and i0 is the nearest integer number to m/[4log(n/m)]. Let us replace the updating scheme εk+1= εk/2 by (7.30), and redo the aforementioned experiments. The results (for p = 0.5) were summarized in Figure 7.2, from which it can be seen that reweighted algorithms still outperform the standard ℓ1-minimization, but this time CWB, NW1, and NW4 are quite comparable to each other, and they perform better than NW2, NW3, and Wlp under the updating scheme (7.30).
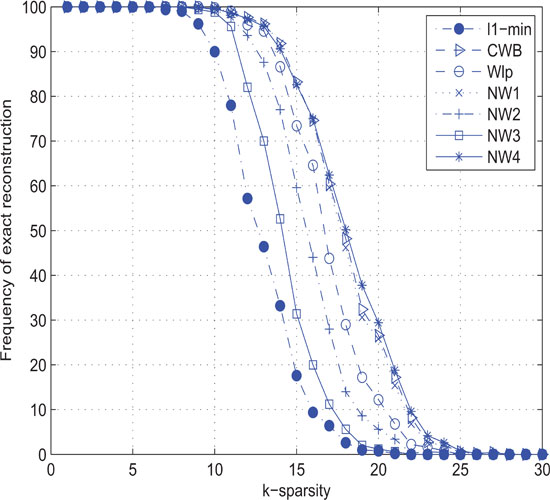
Figure 7.2: Success rates of seven algorithms in finding k-sparse solutions of linear ...
Get Sparse Optimization Theory and Methods now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

