Chapter 3. Numbers and Dates
This chapter covers recipes for working with Scala’s numeric types, and it also includes recipes for working with the Date and Time API that was introduced with Java 8.
In Scala, the types Byte, Short, Int, Long, and Char are known as integral types because they are represented by integers, or whole numbers. The integral types along with Double and Float comprise Scala’s numeric types. These numeric types extend the AnyVal trait, as do the Boolean and Unit types. As discussed on the unified types Scala page, these nine types are called the predefined value types, and they are non-nullable.
The relationship of the predefined value types to AnyVal and Any (as well as Nothing) is shown in Figure 3-1. As shown in that image:
-
All of the numeric types extend
AnyVal. -
All other types in the Scala class hierarchy extend
AnyRef.
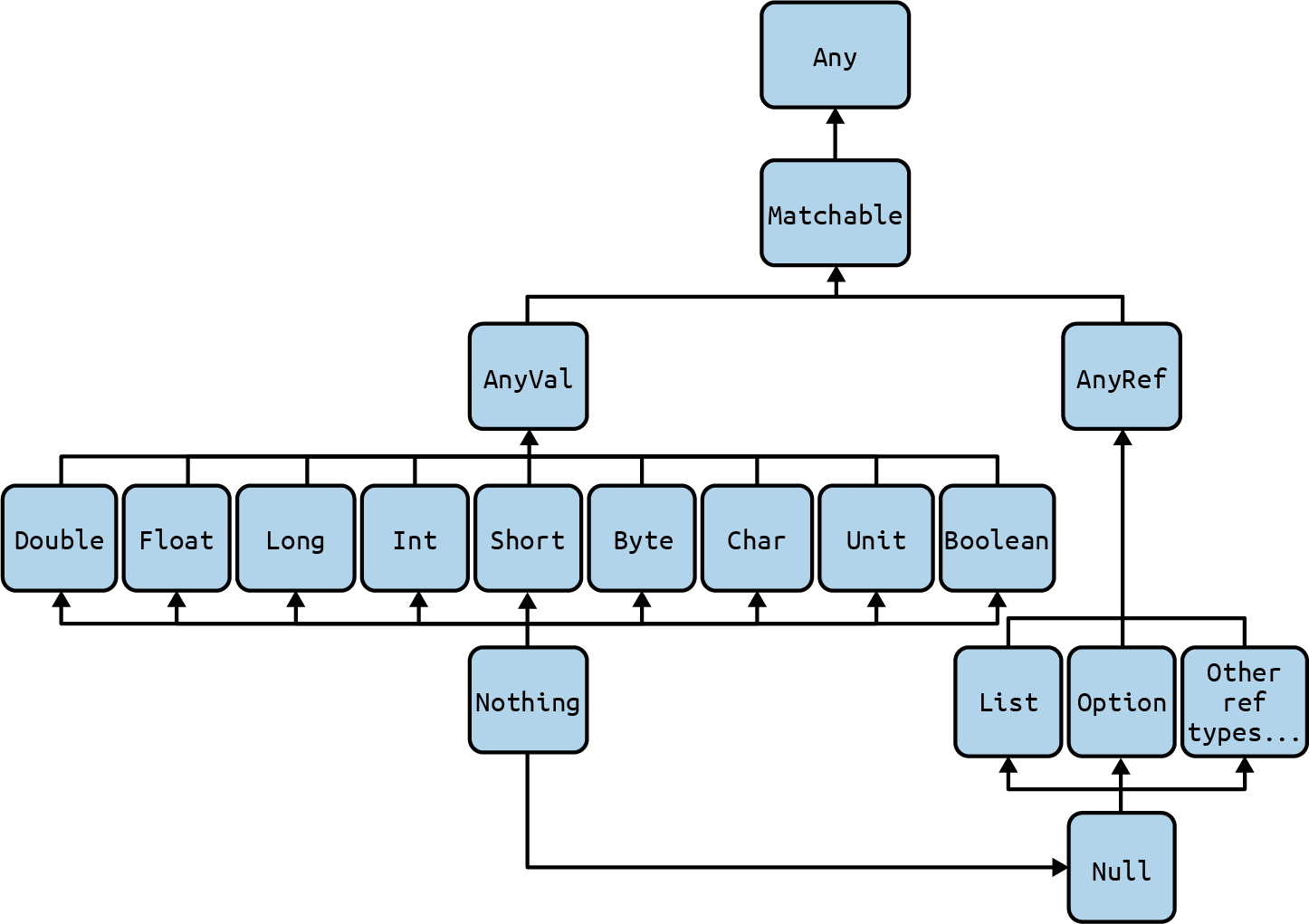
Figure 3-1. All the predefined numeric types extend AnyVal
As shown in Table 3-1, the numeric types have the same data ranges as their Java primitive equivalents.
| Data type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
|
16-bit unsigned Unicode character |
0 to 65,535 |
|
8-bit signed value |
–128 to 127 |
|
16-bit signed value |
–32,768 to 32,767 |
|
32-bit signed value |
–2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
|
64-bit signed value |
–263 to 263–1, inclusive (see below) |
|
32-bit IEEE ... |
Get Scala Cookbook, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

