This kind of traversal starts from the root of a tree and visits the node from one level of the tree to the other:
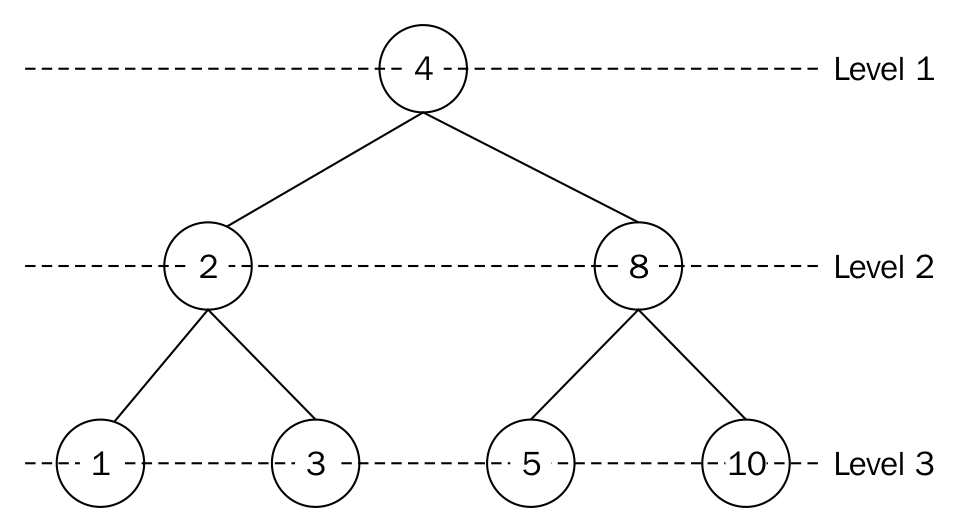
The node at level 1 is node 4. We visit this node by printing out its value. Next, we move to level 2 and visit the nodes on that level, which are nodes 2 and 8. On the last level, level 3, we visit nodes 1, 3, 5, and 10.
The complete output of such a traversal is 4, 2, 8, 1, 3, 5, and 10.
This mode of traversal is made possible by using a queue data structure. Starting with the root node, we push it into a queue. The node at the front of the queue is accessed (dequeued) and either printed and stored for ...

