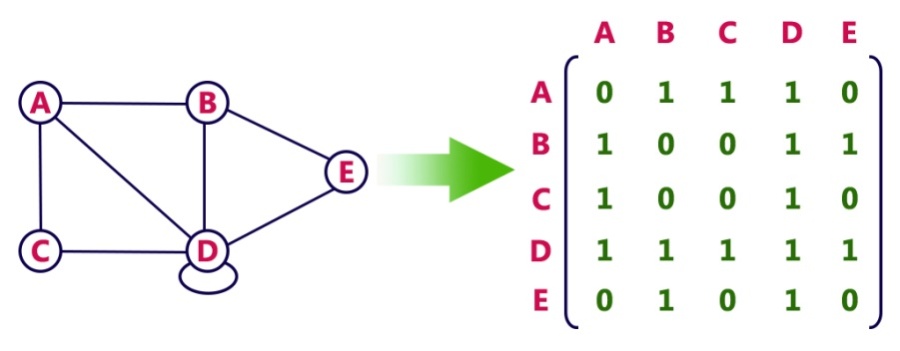
In an adjacency matrix, we represent the graph in a two-dimensional array, where each node represents the array index horizontally and vertically. If the edge from A to B is directional, then we mark that array index [A][B] to 1 to mark the connection; otherwise, it's 0. If the edge is not directional, then both [A][B] and [B][A] are set to 1. If the graph is a weighted graph, then [A][B] or [B][A] will store the weight instead of 1. The following diagram shows the undirected graph representation using a matrix:
This one shows the directed graph representation of the matrix:
Though our graph representation shows an alphabetic ...

