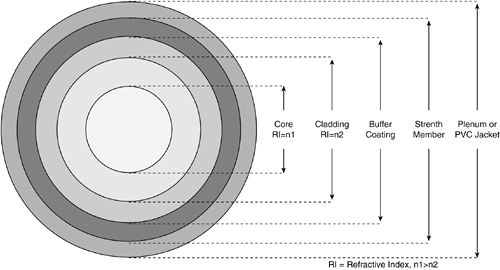
The Physics Behind Fiber Optics
A fiber-optic cable is composed of two concentric layers, called the core and the cladding, as illustrated in Figure 3-1. The core and cladding have different refractive indices, with the core having a refractive index of n1, and the cladding having a refractive index of n2. The index of refraction is a way of measuring the speed of light in a material. Light travels fastest in a vacuum. The actual speed of light in a vacuum is 300,000 kilometers per second, or 186,000 miles per second.
The index of refraction is calculated by dividing the speed ...
Get Optical Network Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.