65G-NR Radio Interface – MIMO and Beamforming
6.1. Multiplexing techniques
6.1.1. MIMO mechanism
The MIMO mechanism improves radio data rate by performing spatial multiplexing of multiple signals. Each signal is transmitted on several antennas and received on multiple antennas, and all signals share the same time–frequency resource.
SU-MIMO (Single User – Multiple Input Multiple Output) refers to the transmission from a base station to one mobile, using the same frequency and time resource, on two antennas (2x2 MIMO) (Figure 6.1), on four antennas (4x4 MIMO) or on eight antennas (8x8 MIMO).
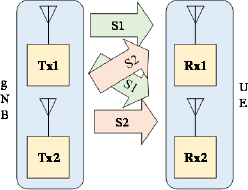
Figure 6.1. SU-MIMO mechanism
MU-MIMO (Multi User – MIMO) refers to the transmission from a radio node to different mobiles, using the same frequency and time resource, on two antennas (2x2 MIMO) (Figure 6.2), on four antennas (4x4 MIMO) or on eight antennas (8x8 MIMO).
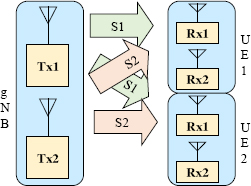
Figure 6.2. MU-MIMO mechanism
The receivers receive the components y1 and y2 which are the product of the components x1 and respectively x2 (the signals transmitted) by the transmission matrix H. The signal x1 (respectively x2) is transmitted by the transmitter Tx1 (respectively Tx2). The signal y1 (respectively y2) is received by the receiver Rx1 (respectively Rx2). The transmission matrix H contains the transfer functions ...
Get NG-RAN and 5G-NR now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

