The std::vector template has one special case: std::vector<bool>. Since the bool datatype has only two possible values, the values of eight bools can be packed into a single byte. std::vector<bool> uses this optimization, which means that it uses eight times less heap-allocated memory than you might naturally expect.
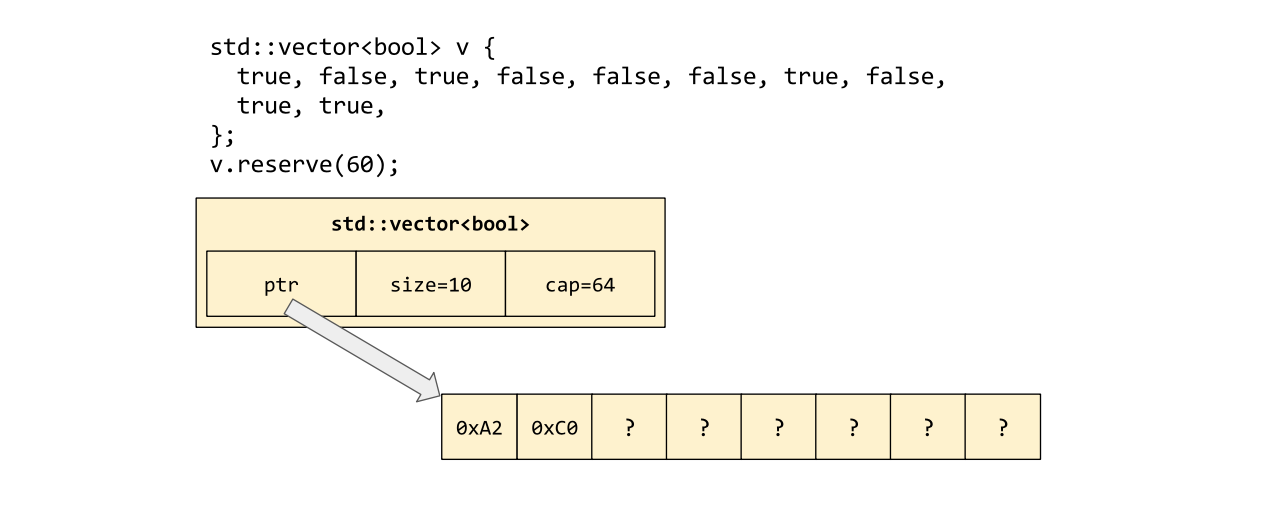
The downside of this packing is that the return type of vector<bool>::operator[] cannot be bool&, because the vector doesn't store actual bool objects anywhere. Therefore, operator[] returns a customized class type, std::vector<bool>::reference, which is convertible to bool but which is not, itself, ...

