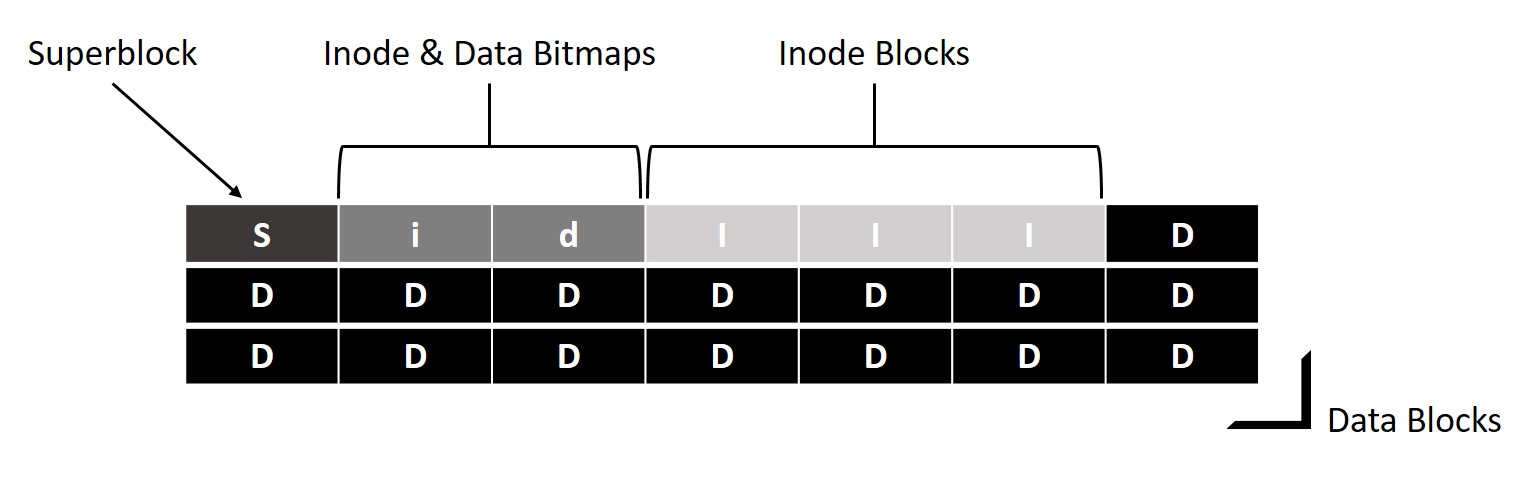
Apart from storing inodes that captures metadata of individual files, filesystems also need to maintain metadata pertaining to disk volume as a whole, such as size of the volume, total block count, current state of filesystem, count of inode blocks, count of inodes, count of data blocks, start inode block number, and filesystem signature (magic number) for identity. These details are captured in a data structure called superblock. During initialization of filesystem on disk volume, the superblock is organized at start of disk storage. The following diagram illustrates the complete layout of disk storage with superblocks: