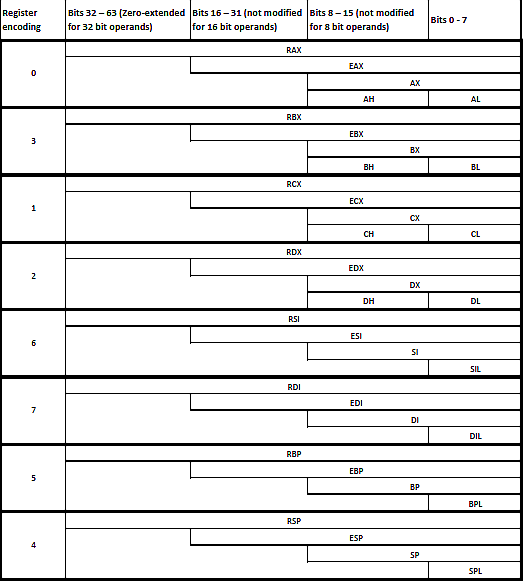
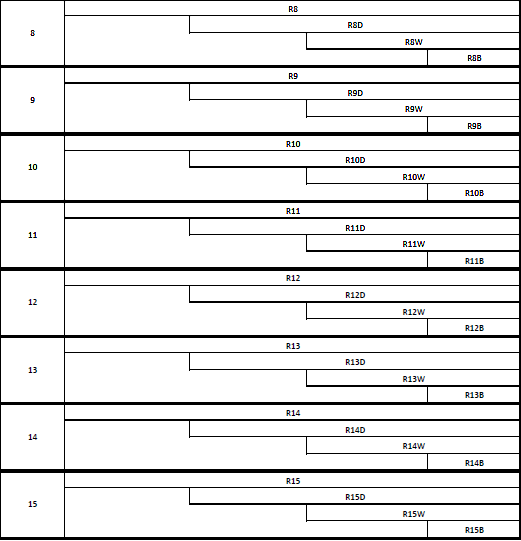
Depending on the mode of the operation (protected or long), there are 8 to 16 available general purpose registers in modern Intel processors. Each register is divided into subregisters, allowing access to data with a bit width lower than the width of the register.
The following table shows general purpose registers (further referred to as GPR):