This case occurs when the height of a node’s left child becomes greater than that of the right child, and the left child is right-heavy. In this case, we can fix it by doing a left rotation on the left child, which results in the left-left case, then we fix it again by doing a right rotation on the unbalanced node ,as demonstrated by the following diagram:

Let’s use a practical example. Consider the following diagram:
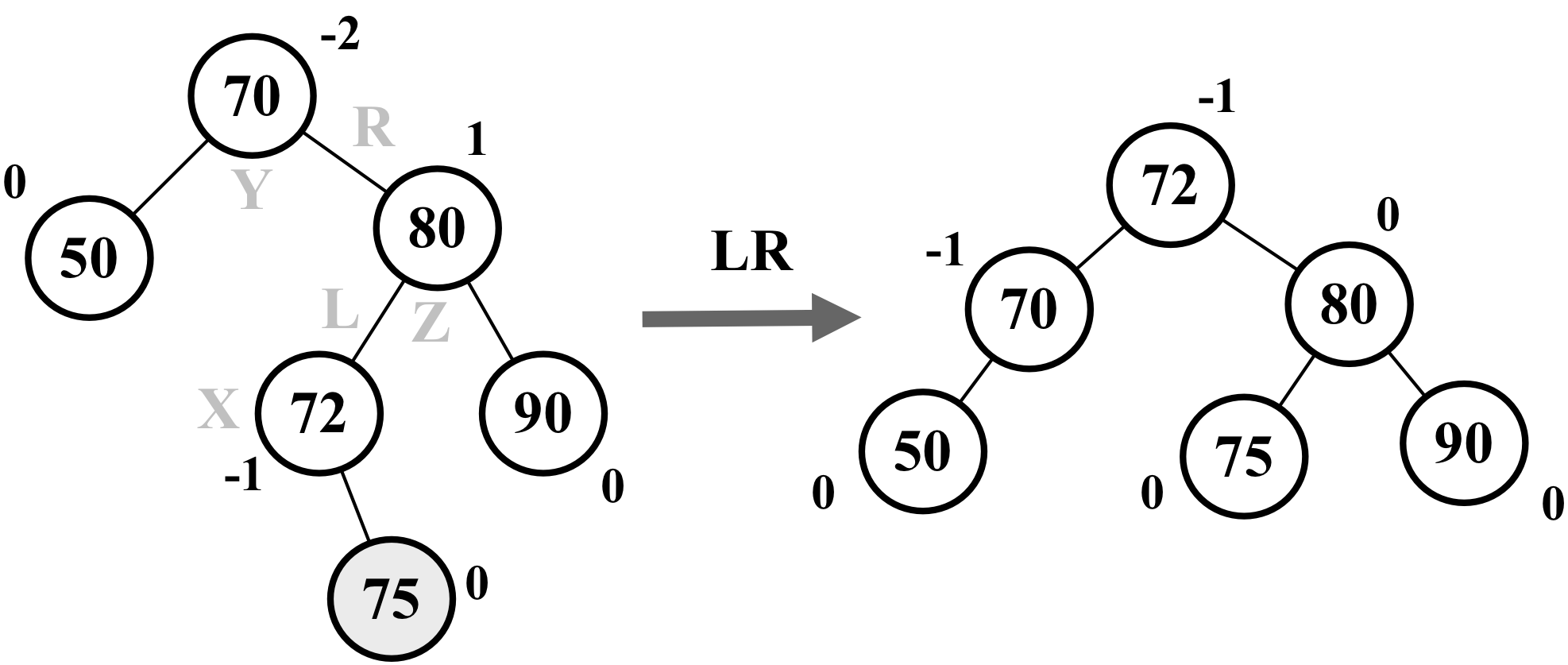
Suppose node 75 was the last one inserted in the AVL tree. This would make the ...

