Exceptions were discussed in the previous chapter. To handle an exception, the code has to be placed between the try and catch blocks. Multiple exceptions can be defined. A few exceptions are mentioned in the following class diagram:
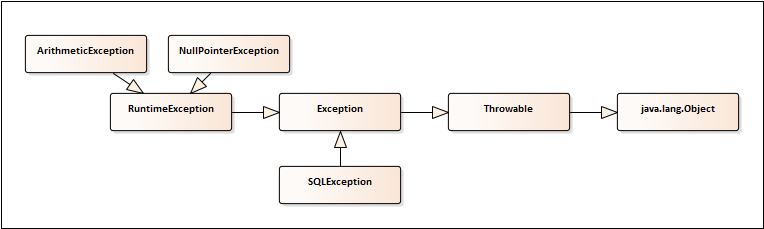
Here's an example code that deliberately causes a division by zero error:
try { System.out.println(0/0); System.out.println("exit"); } catch (NullPointerException e) { System.out.println("NULL POINTER EXCEPTION!"); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("DIFFERENT ERROR"); }
This will print the following: ...

