13.8 Calibration and Linearity Study of the Measurement System
Retrieve the worksheet file: GAGELIN.MTW and do the following.
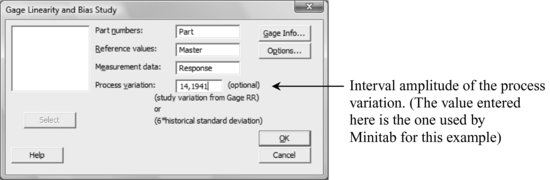
Stat > Quality Tools > Gage Study > Gage Linearity and Bias Study
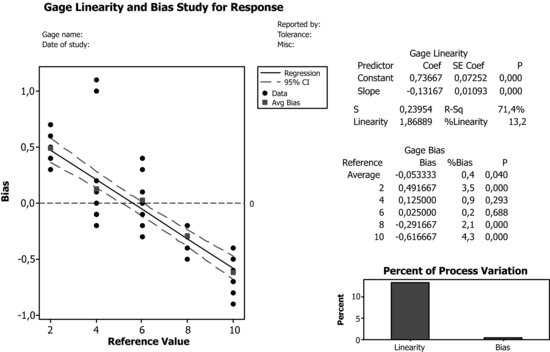
Where Does the Output Information of the Linearity Study Come from and How to Interpret It?
| Graph: | Shows the difference between the measured value and the real one (Bias), versus the real value (Reference). It may also be drawn by placing the difference between C3 (Response) and C2 (Master) in column C4 (named Difference) and then choosing: |
| Stat > Regression > Fitted Line Plot |
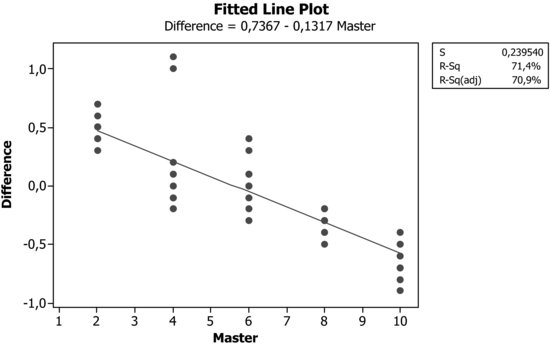
| Linearity: | Product of the slope of the regression line times the amplitude of the process variation. Thus, in our case: |
| Linearity = 0.13167×14.1941 = 1.8689. | |
| %Linearity | Slope of the regression line multiplied by 100. Here, the variation due to linearity is equivalent to 13% of the total variation. |
| Bias: | In the first line, the average of all differences between the measured and reference values is shown (corresponding in this case to the mean of column C4). Just beneath, the corresponding deviations ... |
Get Industrial Statistics with Minitab now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

