The following is a diagram of the abstract example we covered back in Chapter 2, Task Signaling and Communication Mechanisms:
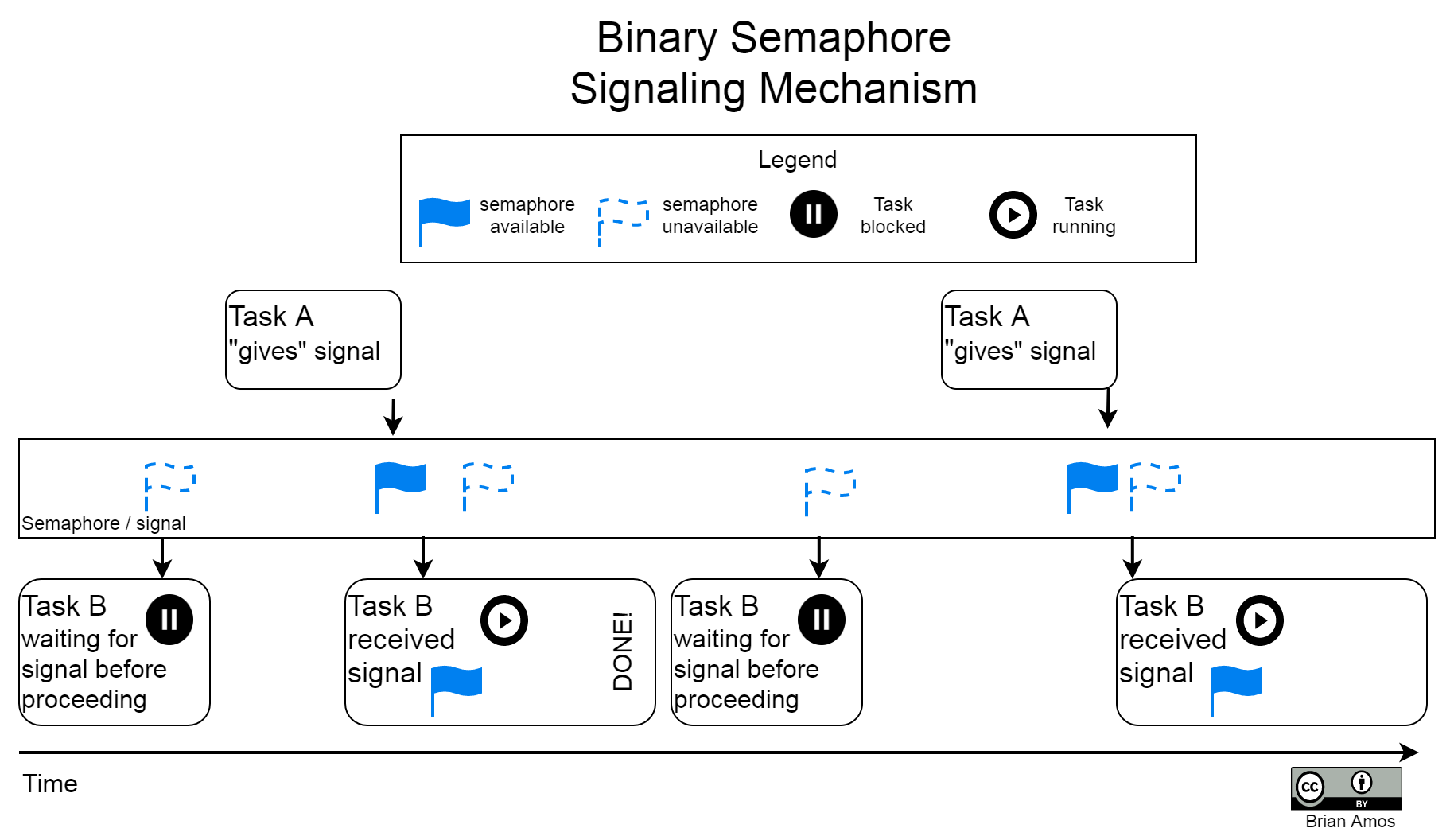
The preceding diagram shows TaskB waiting on a semaphore from TaskA. Each time TaskB acquires the desired semaphore, it will continue its loop. TaskA repeatedly gives a semaphore, which effectively synchronizes when TaskB runs. Now that we have a full development environment set up, let's take a look at what this looks like with some actual code. Then, we'll run it on hardware and blink a few LEDs to see exactly what this behavior looks like in the real world.

