The Euclidean distance can be defined as the length of the line segment joining the two data points plotted on an n-dimensional Cartesian plane. For example, consider two points plotted in a 2D plane:
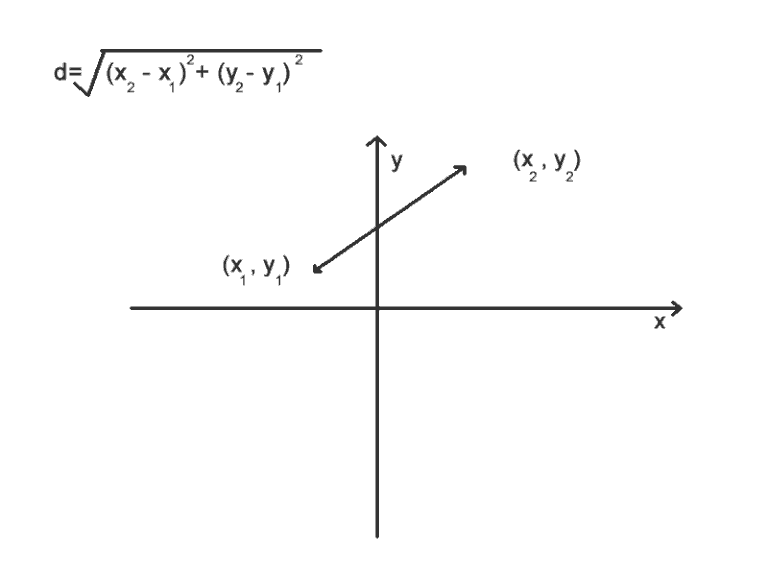
The distance, d, between the two points gives us the Euclidean distance and its formula in the 2D space is given in the preceding graph.
More generally, consider two n-dimensional points (or vectors):
- v1: (q1, q2,...., qn)
- v2: (r1, r2,....., rn)
Then, the Euclidean score is mathematically defined as:


