The ordered crossover (OX1) method strives to preserve the relative ordering of the parent's genes as much as possible. We will demonstrate it using chromosomes with a length of six.
The first step is a two-point crossover with random cut points, as shown in the following diagram (with the parents depicted on the left side):
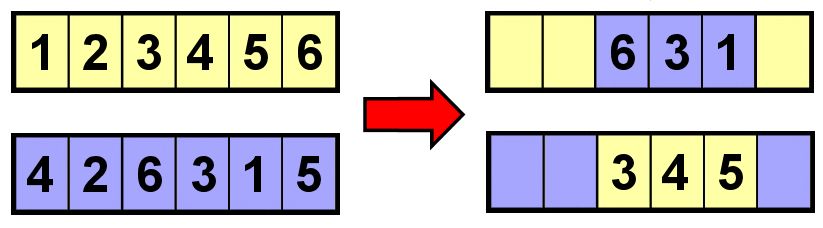
We will now start filling in the rest of the genes in each offspring by going over all the parent's genes in their original order, starting after the second cut point. For the first parent, we find a 6, but this is already present in the offspring, so we continue (with ...

