Chapter 20. T
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is featured in the internet protocol suite. All packets sent through computer networks use TCP or UDP (User Datagram Protocol). UDP is a simpler protocol which lacks the upper layer protocol indications for message delivery that TCP uses. Most of the packets that are sent to and from your phone or PC through the internet are TCP packets—sections of data that are transmitted across computer networks of all kinds.
In TCP, ACK is a command used to establish a connection between an endpoint (such as your phone or PC) and a server. This is called the “three-way handshake.”
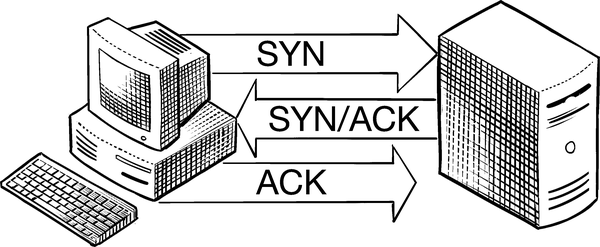
Here’s how the three-way handshake works. First, a client (the endpoint) sends a SYN command to a server. If the server processes the SYN command successfully, it’ll send the client a packet with the SYN-ACK command. If that’s successful, the client sends the server a packet with ACK. SYN is for establishing a data sequence, and ACK means “acknowledged!”
When the client is ready to close a connection to a server, it sends the server a packet with FIN. The server responds with ACK. Then the server sends a packet with SYN, and the client responds to the server with ACK. You guessed it, FIN means “finish.”
Every time your phone or PC successfully downloads web pages from the internet in your web browser, ...
Get Hacker Culture A to Z now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

