The Seven Domains of a Typical IT Infrastructure
What role do the three tenets of systems security play in a typical IT infrastructure? First, let’s review what a typical IT infrastructure looks like. Whether in a small business, large government body, or publicly traded corporation, most IT infrastructures consist of the seven domains shown in FIGURE 1-9: User, Workstation, LAN, LAN-to-WAN, WAN, Remote Access, and System/Application Domains.
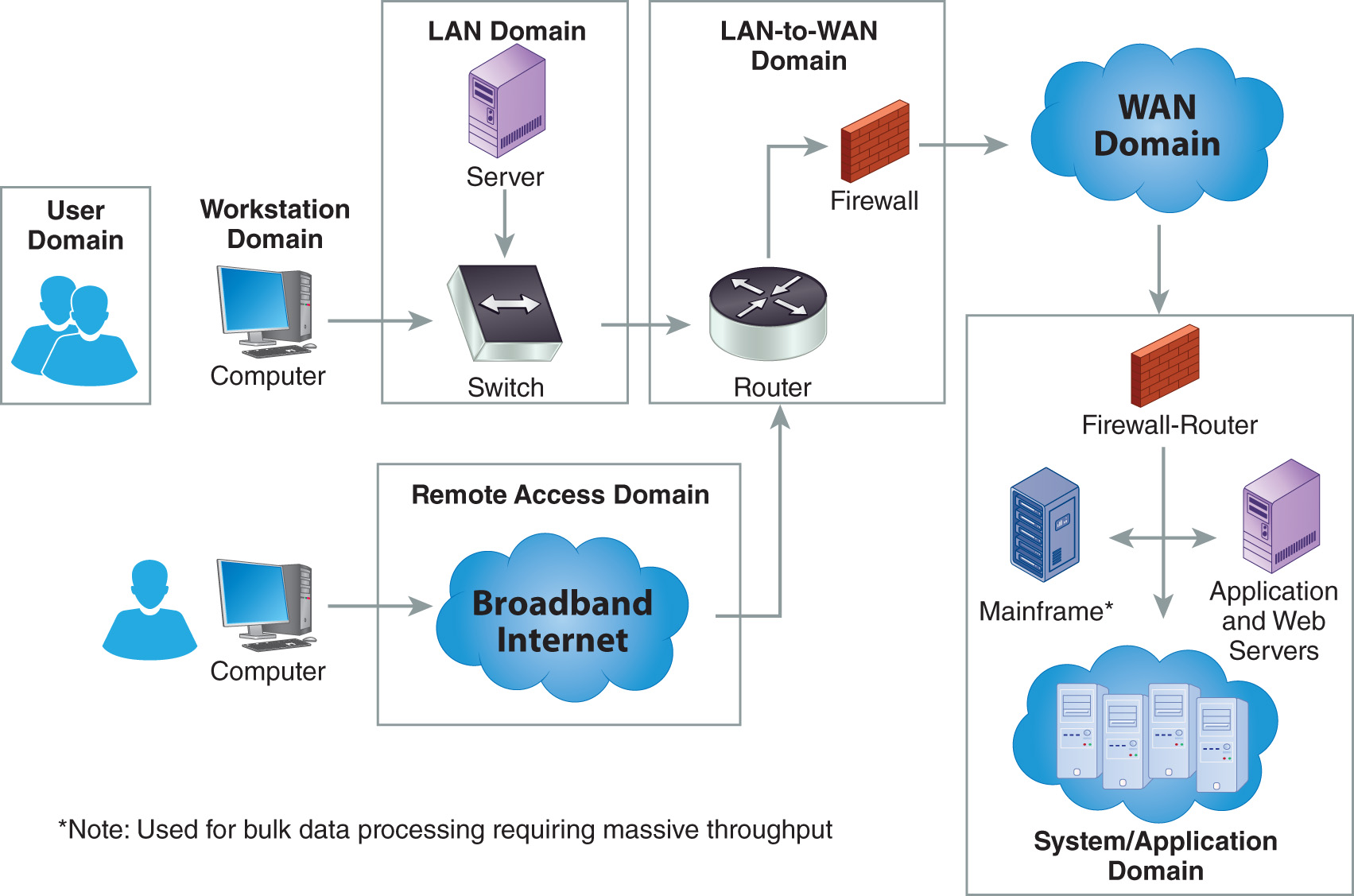
FIGURE 1-9 The seven domains of a typical IT infrastructure
Each domain requires proper security controls, which must meet the requirements of the C-I-A triad. Following is an overview of the seven domains ...
Get Fundamentals of Information Systems Security, 4th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

