12The Cloud Continuum and Industry 4.0
Transformations in the industrial world happen in spurts when a new revolutionary solution comes along. We are at the fourth revolution with Industry 4.0. Figure 12.1 lists these different stages to arrive at the fourth one, whose objective is to totally automate industrial production from the product order to its delivery.
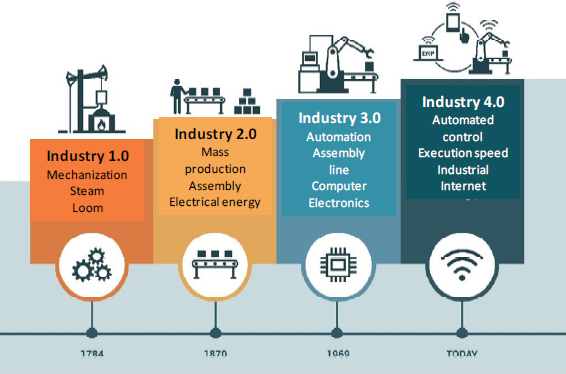
Figure 12.1. Revolutions in the industrial world.
The revolution brought about by Industry 4.0 comes from the mutations due to digital technology. The control of industrial equipment, such as robots or smart sensors, falls into this category, where real-time and remote control are paramount. This industrial revolution is based on automated systems that can be activated in real time. Many important changes are needed in manufacturing, engineering, use of new materials, supply chain and lifecycle management. Smart factories must be particularly flexible and automated. Services and applications must be combined with platforms that enable the automation of the environment, which will also be used for communication between people, objects and systems. Latency requirements for different applications in the automated manufacturing world range from tens of milliseconds for mechanical, to milliseconds for M2M (Machine-to-Machine) communications, to 1 ms for electrical devices. Reaction times for control cycles of fast-moving ...
Get Cloud and Edge Networking now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

