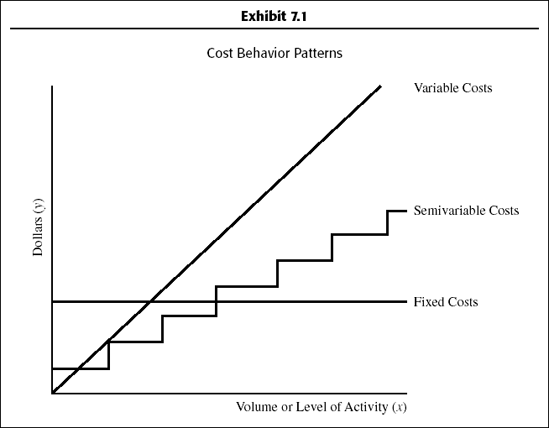
7.2. Analysis of Mixed (Semivariable) Costs
For forecasting, planning, and budgeting, mixed costs need to be separated into their variable and fixed components. Because the mixed costs contain both fixed and variable elements, the analysis takes this mathematical form, which is called a cost-volume formula (or flexible budget formula):
- Y = a + bX
- Where Y = the mixed cost to be broken up
- X = any given measure of activity such as direct labor hours, machine hours, or production volume
- a = the fixed cost component
- b = the variable rate per unit of X
Separating the mixed cost into its fixed and variable components is the same thing as estimating the parameter values a and b in the Y = a + bX formula. Several methods can be used for this purpose, including the high-low method and regression analysis. They are discussed next.
Get Budgeting Basics and Beyond now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

