The transaction data is recorded in files, and these files are known as blocks. The blocks are stacked on top of one another, the most recent block being at the top. The following table depicts the structure of the block and the size of the elements in a block:
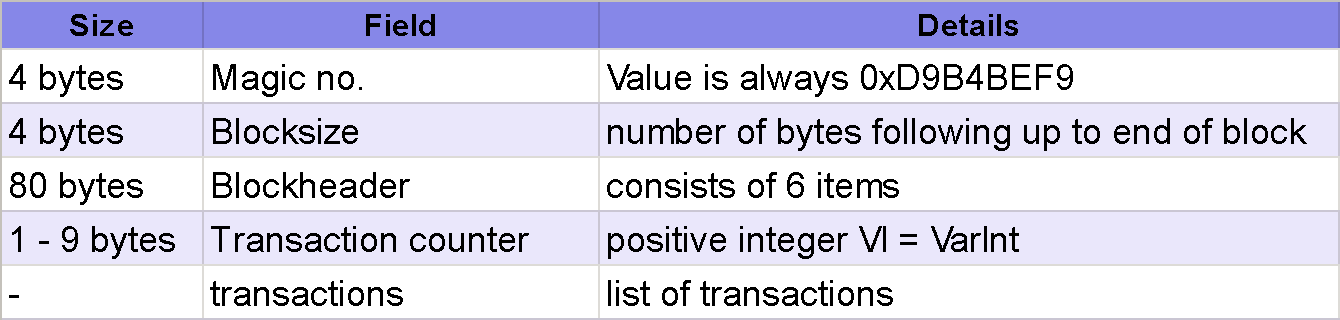
Every block in the Bitcoin network has almost the same structure, and each of the blocks is chained to the most recent block. These are the fields of the block:
- Magic number: This number is an identifier for the blockchain network. Its value is always constant at 0xD9B4BEF9. It confirms the start of the block and verifies that the data is from the production network.
- Block size ...

