Appendix AComplex Modulus of Typical Damping Treatments
This appendix presents a brief summary of the effect of operating temperature and frequency on the complex modulus of three of the most commonly used viscoelastic materials (VEM). These VEMs are manufactured by 3M (Bonding Systems Division, 3M Center, Building 220‐7E‐01, St. Paul, MN 55144‐1000), E.A.R. (Aearo E.A.R. Specialty Composites, 7911 Zionsville Road Indianapolis, IN 46268), and Soundcoat (Soundcoat, 1 Burt Drive, Deer Park, NY 11729).
A.1 3MTM Viscoelastic Damping Polymers
The main characteristics of the ISD series (110,112, 113) of 3M VEM are summarized in Table A.1 and Figures A.1–A.3.
Table A.1 Operating temperature range, maximum loss factor, and corresponding storage modulus of 3M VEM (ISD 110, 112, 113).
| Polymera,b,c | Operating temperature range (°C) | Maximum loss factor η max at temperature (°C) | Storage shear modulus G ′ at η max (MPa) |
| ISD 110 | 40 to 105 (high) | 1.2 at 55 | 0.12 |
| ISD 112 | −20 to 65 (normal) | 1.1 at 30 | 0.15 |
| ISD 113 | −40 to 20 (low) | 1.2 at −20 | 0.40 |
a 3M, Bonding Systems Division, 3M Center, Building 220‐7E‐01, St. Paul, MN 55144‐1000.
b Poisson's ratio for 110, 112, and 113 viscoelastic damping polymers: approximately 0.49.
c Density for 110, 112, and 113 viscoelastic damping polymers: approximately 0.9–1.0 g cm−3.
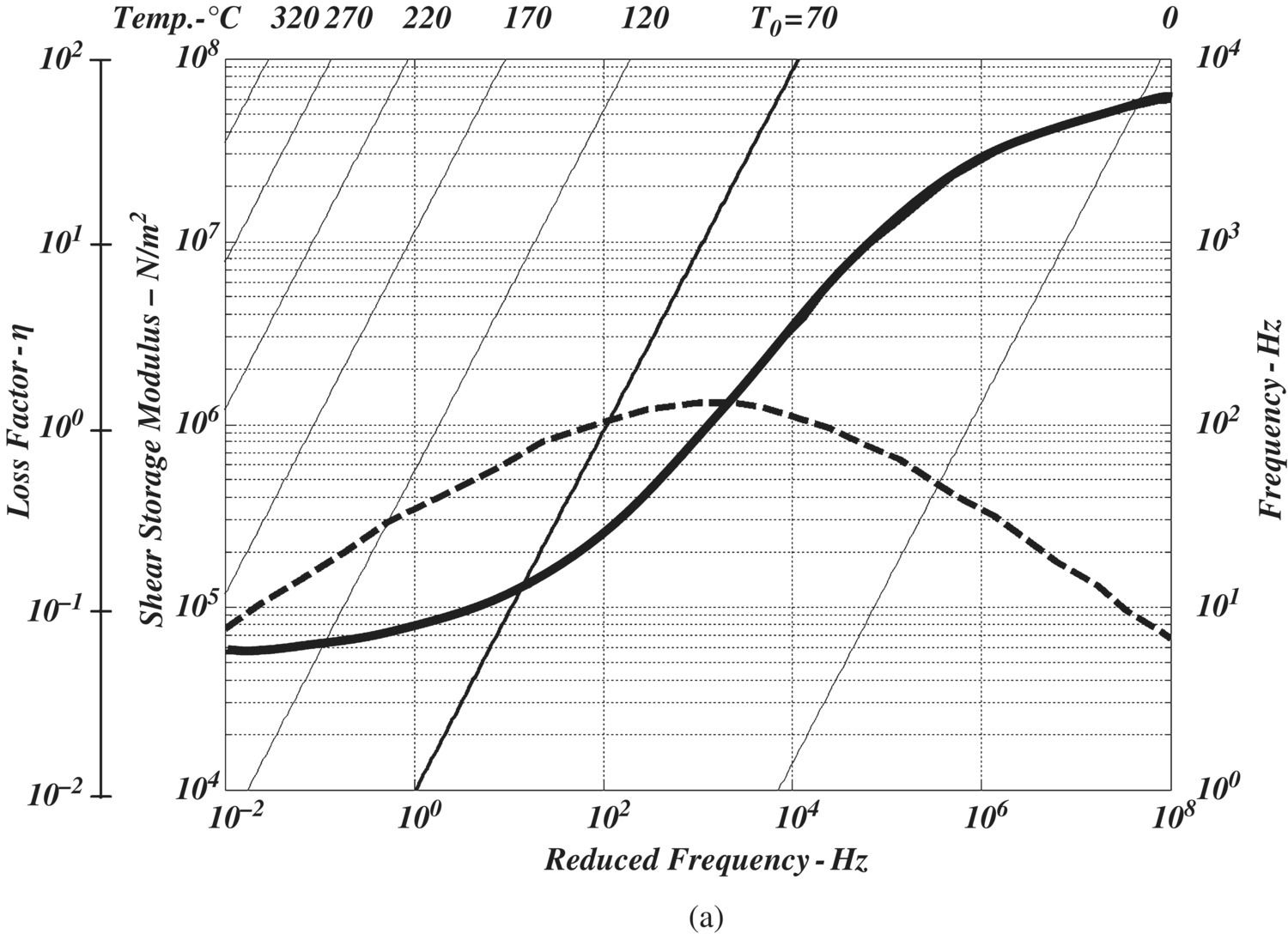
Figure A.1 Complex modulus of ISD‐110 (T0 = 70 °C).
Get Active and Passive Vibration Damping now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

