The following steps are involved in hierarchical clustering:
We create a separate cluster for each data point in our problem space. If our problem space consists of 100 data points, then it will start with 100 clusters.
We group only those points that are closest to each other.
We check for the stop condition; if the stop condition is not yet satisfied, then we repeat step 2.
The resulting clustered structure is called a dendrogram.
In a dendrogram, the height of the vertical lines determines how close the items are, as shown in the following diagram:
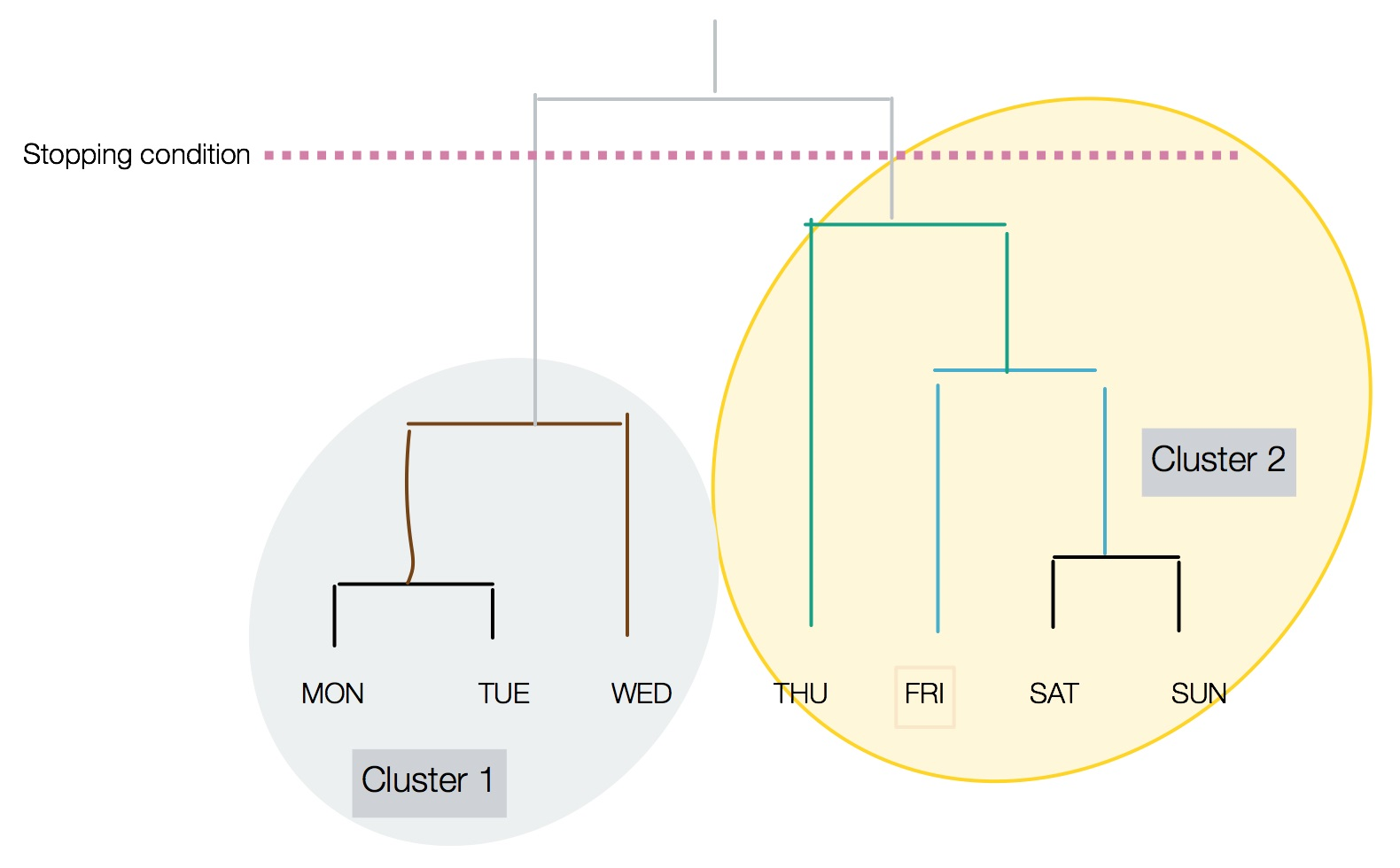
Note that the stopping condition is shown as a dotted ...

